PLAČIAJUOSČIŲ TERAHERCŲ DAŽNIO IMPULSŲ GENERAVIMAS IR CHARAKTERIZAVIMAS
Detali informacija
Ištrauka
PLAČIAJUOSČIŲ TERAHERCŲ DAŽNIO IMPULSŲ GENERAVIMAS IR CHARAKTERIZAVIMAS
BAKALAURO STUDIJŲ BAIGIAMASIS DARBAS
Table of contents
Introduction 4
1.Methods for generation and detection of short THz pulses 5
2.THz radiation generation in plasma induced by two-color femtosecond pulses 6
3.Setups for THz generation and characterization 9
4.Parameters of the setup used for THz characterization 12
5.Spatial and energy properties of generated THz radiation 13
6.Spectral measurements of THz radiation 15
Conclusions 20
Literature 21
Summary 24
Santrauka 25
Introduction
Terahertz (THz) radiation, which occupies a range of frequencies from 0.1 THz to 10 THz, is
becoming more and more popular for scientific research in the recent years due to its unique
properties that lead to versatile applications. THz radiation can penetrate materials like carboard,
paper, plastic, cloth and leather with little losses. It is also not dangerous to humans in comparison
to ionizing X-ray radiation. Due to these features THz radiation is currently being used in medicine,
spectroscopy, quality control, security scanning, etc. [1–4]. For example, THz radiation can detect
concealed explosives without exposing a person to harmful radiation, since materials have specific
THz absorption peaks from which they can be recognized [5]. However, scientists are still looking
for efficient and reasonably priced methods for THz radiation generation [6]. Many different
generation methods are being explored, however one of the most promising ones is THz emission
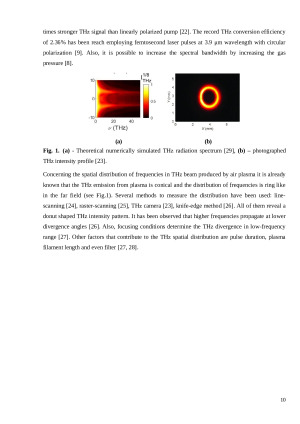
from laser induced plasma in air. This THz generation technique was discovered by Cook and
Hochstrasser in 2000 [7]. It provides THz radiation that has high energy (>5 μJ), is
ultra-broadband (0.1 THz – 75 THz) [8], and can have high conversion efficiency [9]. Since, this
method is currently being thoroughly investigated to further improve the efficiency of THz
generation, it is important to understand one key aspect of it - spatio-temporal distributions inside
the THz beam. Measuring these distributions can facilitate theoretical modelling of THz radiation
generation in laser-created gas plasmas. Therefore, the goal of this work is to experimentally
investigate THz radiation, generated in air plasma by focused bichromatic femtosecond laser pulses,
including the spectral and spatial measurements, as well as to assemble an optical setup for THz
generation and characterization.
1.Methods for generation and detection of short THz pulses
One method for generation of short THz pulses is using a photoconductive antenna. Such a device
typically uses a semiconductor material (for example GaAs, InP, amorphous Si) and a laser as
optical pumping source. The working principal of it is that when the laser illuminates the
semiconductor, electrons are excited, thus electron-hole pairs are generated. Because a bias voltage
is applied to the semiconductor the electric field separates charge carriers and accelerates them. The
acceleration of carriers results in THz pulse emission, which corresponds to the duration of laser
pulses. The resulting THz frequency depends on the semiconductor material, bias voltage and
properties of the pump laser. This method is also used for detection of THz pulses. The principal is
very similar, however this time instead of applying bias voltage to the semiconductor, the THz
pulse induces a voltage, which leads to a current that can be measured. This current will be
proportional to the THz electric field.
Mūsų mokslo darbų bazėje yra daugybė įvairių mokslo darbų, todėl tikrai atrasi sau tinkamą!